| Ultraviolet light : |
| Unlike most disinfectants, ultraviolet (UV) radiation does not inactivate microorganisms by chemical interaction. UV radiation inactivates organisms by absorption of the light which causes a photochemical reaction that alters molecular components essential to cell function. As UV rays penetrate the cell wall of the microorganism, the energy reacts with nucleic acids and other vital cell components, resulting in injury or death of the exposed cells, sterilize them, damaging its reproduction capacity. As a result, UV radiation is exceptional for disinfection of small microorganisms such as dust mites, mold, bacteria and viruses, besides leaves no residual. Sterilization efficiency with UV light reaches up to 99.9% [22]. |
|
|
Next, a UV graphic showing UV ranges:
|
|
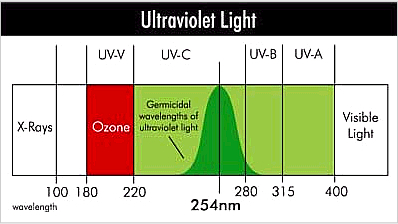 |
|
| Partial list of microorganisms sterilized with UV light: |
|
| Germs: |
|
 |
Staphylocous aureus ATCC 65328 |
 |
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 |
 |
Salmonella typhimurium KTCC 1925 |
 |
Klebsiella pneumniae ATCC 4352 |
 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 |
 |
Escherichia coli ATCC 43895 |
|
| Organisms: |
|
 |
Dermatophagoides farinae |
 |
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus |
|
 |
 |
MRSA(Methicillin Resistance S.aureus) ATCC 3592 |
 |
Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 |
 |
Shigella flexneri ATCC 9199 |
 |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus ATCC 17802 |
 |
Staphylocous aureus ATCC 6538 |
 |
Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 |
 |
Salmonella typhimurium KTCC 1925 |
|
|
|
| Bacteria: |
|
 |
Agrobacterium tumefaciens. |
 |
Bacillus Anthracis. |
 |
Bacillus megaterium (vegitative) |
 |
Bacillus megaterium (spores) |
 |
Bacillus subtilis (vegitative) |
 |
Bacillus subtilis (spores) |
 |
Clostndium tetani. |
 |
Corynebacterium diphtheriae |
 |
Escherichia coll. |
 |
Legionella bozemanil |
 |
Legionella dumofil |
 |
Legionella gormanil |
 |
Legionella micdadel |
 |
Legionella longbeachae |
 |
Proteus vulgaris |
 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (laboratory) |
 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (environment) |
 |
Rhodospilium rubrum |
|
 |
 |
Salmonella enteritidis |
 |
Salmonella paratyphi (enteric fever) |
 |
Salmonella typhimunum |
 |
Salmonella typhosa (typoid fever) |
 |
Sarcina lutea |
 |
Serratia marcescens |
 |
Shigella dysenteriae (dysentery) |
 |
Shigella sonnei |
 |
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
 |
Staphylococcus faecalis |
 |
Legionella pheumophila |
 |
Legionella interrogans (infectius jaundice) |
 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
 |
Neisseria catarrhalis |
 |
Staphylococcus hemolyticus |
 |
Staphylococcus lactis |
 |
Viridans strptococci |
 |
Vibrio cholerae |
|
|
|
| Mold spores: |
|
 |
Aspergilus flavus (yellowish green) |
 |
Aspergilus glaucus (bluish green) |
 |
Aspergilus niger (black) |
 |
Mucor ramosissimus (white gray) |
|
 |
|
 |
Penicillium digitatum (olive) |
 |
Penicillium expensum (olive) |
 |
Penicillium roqueforti (green) |
 |
Rhizopus nigricans (black) |
|
|
|
| Algae: |
|
 |
Chloreila vulgaris (algae) |
|
| Virus: |
|
 |
Bacteriophage (E. coli) |
 |
Hepatitis virus |
|
 |
|
 |
Poliovirus (poliomyelitis) |
 |
Rotavirus |
 |
Tobacco mosaic virus |
|
|
|
| Protozoa: |
|
 |
Nematode eggs |
|
| Yeast: |
|
 |
Baker |
 |
Brewer |
| |
|
|
 |
|
 |
Paramecium |
| |
|
 |
Common yeast cake |
 |
Saccharomyces var. ellipsoideus |
 |
Saccharomyces sp |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Who we are |
|
We are a company that cleans and disinfects fabrics and skin, as well as disinfects and attacks odors in closed spaces. We serve clients from Monterrey, N.L. and its metropolitan area. Our goal is to provide extraordinary care and service when cleaning and disinfecting your mattresses, pillows, rugs, rooms, and any other furniture / vehicle with fabric / skin, and rooms, eliminating mites, mold, pollen, viruses, bacteria and other contaminants, using patented German technology on a global scale, scientifically backed up and 100% natural, free of harm against people, pets and objects. 95% of customers with allergies have reported an improvement in their life quality after our services..
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|









